The answer is: “Pretty screwed.”
Some takeaways:
The answer is: “Pretty screwed.”
Some takeaways:
There’s just enough tank-specific news coming out of the Russo-Ukrainian War to justify a roundup. Despite supposedly having the largest tank army in the world, Russia’s tank corps is clearly taking it on the chin in Ukraine.
#Russia's active tank fleet is actually not 12,000 strong. In reality it is just over 2,500. By active tanks I mean tanks that are actually in service in an organised unit (i.e. a tank battalion, regiment, brigade etc.) and are not undergoing field tests (T-14 Armata). pic.twitter.com/fJYrGjc5L4
— TankDiary (@TankDiary) March 19, 2022
Can Russia pull reserve tanks out of its inventory and put them in active duty? Probably, but: A.) The truck tire issued showed that even active equipment hasn’t been well-maintained. How much worse shape are mothballed vehicles in? B.) How quickly can new tank crews be trained to work effectively? Speaking of maintenance problems:
Russia’s largest tank manufacturer, Uralvagonzavod, has halted production because of supply shortages, according to Ukraine’s state media and Ukrainian armed forces.
The Kyiv Independent writes that Uralvagonzavod has stopped operations in its Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant in west-central Russia because of the lack of component parts supplied from foreign countries.
The claim was initially made by a report of the Armed Forces of Ukraine and confirmed by the Ukrainian Ministry of Defense on March 21, according to The Kyiv Independent.
Uralvagonzavod had his assets frozen in the U.K. on February 24 and was hit by European Union sanctions on March 15.
Two reasons to take this with a few grains of salt: A.) It’s a Ukrainian source, and B.) Uralvagonzavod is the company manufacturing the T-14 Armata tank as well as the T-90M, and they were only supposed to produce 100 T-14s total, of which none have been spotted in-theater.
A LOT OF Russian tanks involved in the invasion of Ukraine have strange cages welded over the roofs of their turrets. Strange and apparently useless—for many pictures have emerged of destroyed vehicles surmounted by them. Sometimes the cage itself has been visibly damaged by an attack that went on to hit the tank beneath.
Stijn Mitzer, an independent analyst based in Amsterdam, has looked at hundreds of verified photographs of destroyed Russian vehicles. He thinks that, far from acting as protection, the cages have done nothing save add weight, make tanks easier to spot, and perhaps give a false and dangerous sense of security to the crew inside. They have thus been mockingly dubbed by some Western analysts as “emotional-support armour” or “cope cages”.
Snip.
The new cages, the fitting of which seems to have begun late in 2021, appear to be a variant of so-called slat or bar armour. Such armour can provide effective lightweight protection if used correctly (as it is, for example, on American Stryker armoured personnel carriers). But in this case that seems not to have happened. They might thus be seen as symbols of Russia’s inadequate preparation for the campaign, as pertinent in their way as its failures to neutralise Ukraine’s air defences and to shoot down that country’s drones.
One of the main threats to armoured vehicles are HEAT (High Explosive Anti-Tank) weapons, such as the Russian-made but widely employed RPG-7. The warheads of these rocket-propelled grenades are shaped charges—hollow cones of explosive lined with metal. When the explosive detonates it blasts the metal lining into a narrow, high-speed jet that is able to punch through thick steel. According to Dr Appleby-Thomas an RPG-7 can penetrate 30cm of steel plate.
And RPG-7s are the babies of the bunch. Other, far more powerful shaped-charge anti-tank weapons used by Ukrainian forces include Javelins supplied by America, NLAWs (Next-generation Light Anti-tank Weapons) supplied by Britain, and drone-borne MAM-L missiles, supplied by Turkey.
HEAT warheads may be countered by what is known as explosive reactive armour, or ERA. When this is hit, a sheet of explosive sandwiched inside it blows up and disrupts an incoming warhead before it can detonate. Many Russian tanks are indeed fitted with ERA. However ERA may, in turn, be defeated by a so-called tandem warhead, in which a small precursor charge triggers the armour’s explosive before the main warhead detonates.
Slat and bar add-on armours are a lighter and cheaper way to counter RPGs, though even if used correctly they are, literally, hit or miss protection. The spacing of the bars or slats is crucial. If a rocket hits a bar it makes little difference, for its warhead will detonate anyway. But if it gets trapped between bars it will probably be damaged in a way which means that the signal from the nose-mounted fuse cannot reach the detonator.
This approach is known as statistical armour, because the protection it offers is all or nothing. It is typically quoted as having a 50% chance of disrupting an incoming RPG. But Dr Appleby-Thomas notes that it works only against munitions with a nose fuse, which Javelins, NLAWs and MAM-Ls do not have.
Russia has been fitting slat armour to vehicles since 2016, but the design of the new cages, seemingly improvised from locally available materials, is baffling. They appear to be oriented in a way that protects only against attacks from above. In principle, that might help against Javelins, which have a “top attack” mode in which they first veer upwards and then dive to punch through a tank’s thin top armour. But, as Nick Reynolds, a land-warfare research analyst at RUSI, a British defence think-tank, notes, even if the cage sets off a Javelin’s precursor warhead, the main charge is still more than powerful enough to punch through the top armour and destroy the tank—as the Ukrainian army itself proved in December, when it tested one against a vehicle protected by add-on armour replicating the Russian design. As expected, the Javelin destroyed the target easily.

Enjoy this Sad Trombone gif, unearthed from the archives of the ancient, terrible conflict known only as The Pony Wars
Despite amassing an invasion force of nearly 200,000 troops and thousands of armored vehicles supported by combat aircraft and warships, the Russian military has failed to reach its primary objectives in the three weeks since its offensive into Ukraine began.
Russian military planners expected a blitzkrieg campaign that would last 48 to 72 hours and lead to a quick Ukrainian capitulation, but Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has led a fierce resistance, and major urban centers, including the capital, Kyiv, remain in Ukrainian hands, surprising Moscow and indeed the world.
Ukrainians’ grit and knowledge of the battlefield have played a large part in their effective defense, but weapons supplied by NATO and EU countries have also played a critical role in stalling the Russian advance.
Ukraine has received billions of worth of weapons from the West — the US has provided $1 billion in security assistance just this week — and among that aid, three weapon systems stand out.
Since the invasion began, US-made FGM-148 Javelins and FIM-92 Stingers and the Next Generation Light Anti-Tank Weapon (NLAW) designed by Britain and Sweden have been the terror of Russian troops.
Tanks and armored vehicles are at the heart of the Russian military doctrine.
Actually Russian military doctrine is usually described as artillary-centric, but tanks are a close second in importance.
Russia’s battalion tactical groups — 75% of which have been committed to the invasion, a US official said Wednesday — are largely mechanized formations meant to use heavy firepower to overcome resistance.
But BTGs are vulnerable to anti-tank defenses like the Javelin, a reusable, fire-and-forget guided missile.
Javelins have two parts: a launch tube and a command launch unit, which has the controls and optical sights for day and night use. The Javelin missile’s nose has a homing infrared guidance system that allows the operator to fire the weapon and then relocate in order to dodge return fire.
Snip.
Against a tank or another armored vehicle, the Javelin will strike from a high angle of attack, targeting the top of the vehicle, where the armor is thinnest.
Before the invasion, Russian tankers sought to counter that by building cages on top of their tanks to detonate the Javelin before it struck and reduce its force. Hundreds of destroyed Russian tanks suggest that has not been an effective countermeasure.
Against a stationary target, like a building or bunker, the Javelin will strike from a more direct line of attack.
Snip.
Ukrainian forces have been using the British-supplied NLAW anti-tank weapon. Although less sophisticated than its American counterpart, the NLAW is extremely easy to operate, and with a 150 mm high explosive anti-tank warhead, it’s deadly too.
Like the Javelin, the NLAW can strike targets from above, but its effective range of about 800 meters is more limited than the Javelin’s 2,000-meter range.
Information on Stinger use against Russian aircraft snipped.
The US on Wednesday announced another package of security assistance to Ukraine, which included 800 Stingers and 2,000 Javelins, bringing the total of each provided by the US to 1,400 and 4,600, respectively. The package also includes 1,000 light anti-armor weapons and 6,000 AT-4 unguided, man-portable anti-armor missiles.
The Russian military’s one-off T-80UM2 experimental main battle tank has been knocked out during recent fighting in Ukraine, marking one of the more unusual kills attributed to the country’s defenders, who continue to disrupt the Kremlin’s invasion plans. The fact that this unique fighting vehicle was even participating in combat in Ukraine is somewhat surprising, but it would not be the first example of new or experimental Russian weapons systems being deployed in the campaign.
The team of researchers at the Oryx blog, who have been compiling photo and video evidence of materiel losses on both sides of the conflict, identified the wreckage of the T-80UM2 and stated that it was destroyed on March 17, or that its remains were uncovered on this date. The tank is rumored to have been knocked out in Sumy Oblast, in northeastern Ukraine, apparently in the vicinity of the town of Trostyanets.
The T-80UM2 is said to have been part of a larger column of Russian vehicles that came under attack by the Ukrainian Armed Forces and photos show destroyed trucks alongside the T-80UM2. Its turret was knocked off and its hull burnt out, although it’s not immediately clear how it was hit and by what.
The story of the T-80UM2 is a complicated one, tied up with a new-generation tank project with the project name Objekt 640, better known as the Black Eagle. A mock-up of the Black Eagle appeared as long ago as 1997, at which point it was being promoted for the export market.
By 1998 it had become clear that work was also underway on the T-80UM2, as a further development of the Cold War-era T-80. There seems to be substantial overlap between the T-80UM2 and the Black Eagle, to the point that some sources consider them one and the same. If that’s the case, then the T-80UM2 may very well have been intended to serve as a prototype for the Black Eagle which, as it turned out, never entered production.
As for the T-80UM2, this vehicle was based on an upgraded T-80U chassis, the main new addition being a welded-steel turret with advanced armor protection, including Kaktus explosive reactive armor (ERA), panels of which were also applied to the front of the hull. More Kaktus was fitted to the track skirts, while there were anti-fragmentation screens around the front of the turret.
In its ultimate form, the T-80UM2 was also fitted with the Drozd-2 active protection system, a hard-kill system that uses radar to detect incoming anti-tank rockets and anti-tank missiles, before automatically firing high-explosive fragmentation munitions at them, with the aim of destroying, or at last disabling them, at a distance of 20-30 feet from the tank.
The T-80UM2 featured a different crew arrangement compared to the T-80U, with the gunner seated on the right and the commander on the left of the turret, swapping sides compared to the earlier tank.
Otherwise, the new tank used the same main armament as the earlier T-80 series, with a 125mm 2A45M smoothbore gun, but this was now fed ammunition via an improved type of automatic loading system. The magazine was moved from below the turret to the bustle, at the back of the turret, apparently in response to survivability concerns highlighted during fighting in Chechnya.
In western armies, prototypes are rarely pressed into combat service, they’re generally preserved in tank museums (like Tortoise at Bovington or the T-28 at the Patton Museum of Cavalry and Armor). The fact that this one was pressed into frontline service may suggest a whiff of desperation to throw everything into the fight. Then again, the Russian military has never been known for being overly sentimental…
“Hits” is perhaps too strong, but it did touch down and do some damage right at the I-35/TX-45 flyover in Round Rock, which is about eight miles from my house. It did some damage but I’m not seeing any reports of fatalities thus far. One woman did get pulled from the wreckage of the home she was renting. There were also some power outages.
Some video:
Amazing @KXAN_Weather video of on the ground tornado crossing I-35 in Round Rock @ 45 just north of Austin pic.twitter.com/eJvCsYnsCN
— Evil MoPac (@EvilMopacATX) March 21, 2022
Edited to add: Hearing that over 1,000 homes were damaged in Williamson County total, but still no fatalities. Here’s some drone footage:
Looks like every roofer within 90 miles is going to be very busy…
There are a lot of posts on Twitter postulating a food shortage due to the Russo-Ukranian War. The reasoning goes that, on top of existing supply chain disruptions, Russia and Ukraine were big wheat exporters, and Russia is the world’s biggest fertilizer exporter.
Those are concerns, and I think there’s a real good chance of food shortages…in Russia. That’s the sort of thing that happens when you unplug yourself from the world economy. And Europe might have some disruption, given that they’re net food importers.
But I doubt we’re going to have that problem in the U.S. of A. First, our supply chain problems were started easing when vaccine mandates started getting lifted due to the dread midterm variant. Second, America makes lot of fertilizer ourselves, and Russia isn’t the exclusive source of nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium. (Though a Canadian rail strike might impact the last.) Third, capitalism has a great way of supplying substitute goods if left to its own devices.
More analysis along those lines.
On February 14, the average price of the four commodities was 15.1c per 1000 calories. By March 8, it had risen to 17.4c, an increase of 15.2%. Using the Roberts and Schlenker factor of 7, this implies a 2.2% decrease in available supply of calories. Removing 55 million metric tons of wheat and 30 million metric tons of corn entails a 2.7% reduction in available supply of calories from the big four commodities. (Here’s an Excel file containing these computations.)
So, it seems the markets are banking the world losing about three quarters of Ukrainian and Russian grain exports (2.2/2.7). Given the large increase in winter wheat prices relative to the other commodities, most of the loss is from wheat.
Traders expect this shock to last only a year. Winter wheat futures prices for delivery after July 2023 barely increased after the invasion. The same is true for corn. The spring wheat market was already tight because of last year’s drought and traders expect it to remain tight beyond 2023.
How common are market shocks of this magnitude? Russian and Ukrainian wheat exports were 7.3% of global production in 2020. Wheat production declined 6.3% in 2010, in part due to a drought that reduce Russian production by 20 million metric tons. Similarly large declines also occurred in 1991, 1994, 2003, and 2018.
From the analysis above, the observed price increases are consistent with a 2.2% decrease in available supply of calories from corn, rice, soybeans, and wheat. Similar declines occurred in 2018, in part due to drought in Argentina and lower wheat acreage in Russia, and in 2012, in part due to drought in the US.
The increase in wheat prices will not cause massive increases in the price of American bread. Most of the price of food is determined by the cost of processing, packaging and marketing. The USDA estimates that farm gate sales of food commodities made up 14% of the retail value of food in 2019. If farm prices increase by 50%, then we would expect food in the grocery store to increase by 7%.
(Hat tip: Scott Adams.)
As long as the Biden Administration doesn’t do something criminally stupid (like imposing wage and price controls to fight inflation, or a mandate that 50% of truck drivers be women), the American economy should adapt to prevent any significant food shortages due to the Russo-Ukrainian War.
Of course, government has no shortage of other ways to wreck the economy and make food scarce, and hyperinflation is one of the best…
Some significant changes since the last update, mainly that Russian forces have finally taken Mariupol, allowing Russian forces in the east to linkup through Donetsk. But elsewhere a slow, grinding stalemate seems to prevail.
Here’s the Livemap snapshot:
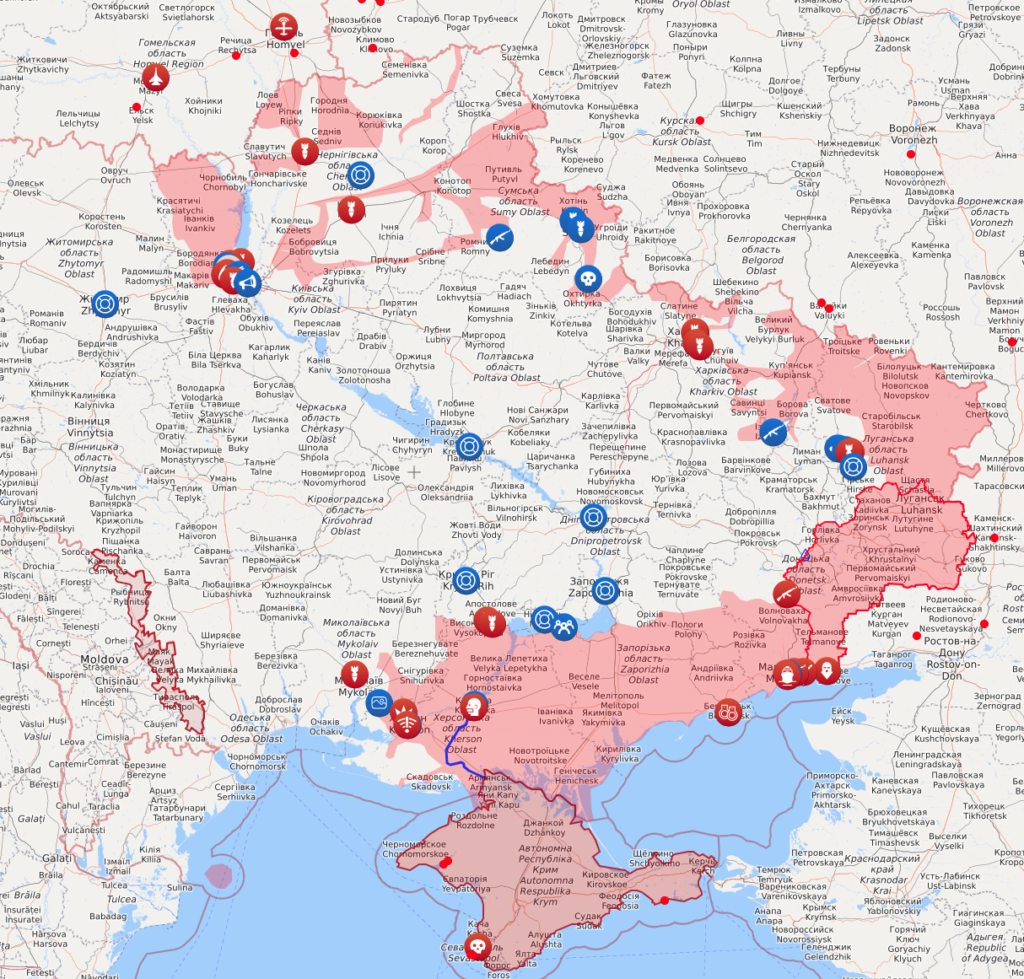
Ukrainian forces have defeated the initial Russian campaign of this war. That campaign aimed to conduct airborne and mechanized operations to seize Kyiv, Kharkiv, Odesa, and other major Ukrainian cities to force a change of government in Ukraine. That campaign has culminated. Russian forces continue to make limited advances in some parts of the theater but are very unlikely to be able to seize their objectives in this way. The doctrinally sound Russian response to this situation would be to end this campaign, accept a possibly lengthy operational pause, develop the plan for a new campaign, build up resources for that new campaign, and launch it when the resources and other conditions are ready. The Russian military has not yet adopted this approach. It is instead continuing to feed small collections of reinforcements into an ongoing effort to keep the current campaign alive. We assess that that effort will fail.
The ultimate fall of Mariupol is increasingly unlikely to free up enough Russian combat power to change the outcome of the initial campaign dramatically. Russian forces concentrated considerable combat power around Mariupol drawn from the 8th Combined Arms Army to the east and from the group of Russian forces in Crimea to the west. Had the Russians taken Mariupol quickly or with relatively few losses they would likely have been able to move enough combat power west toward Zaporizhiya and Dnipro to threaten those cities. The protracted siege of Mariupol is seriously weakening Russian forces on that axis, however. The confirmed death of the commander of the Russian 150th Motorized Rifle Division likely indicates the scale of the damage Ukrainian defenders are inflicting on those formations. The block-by-block fighting in Mariupol itself is costing the Russian military time, initiative, and combat power. If and when Mariupol ultimately falls the Russian forces now besieging it may not be strong enough to change the course of the campaign dramatically by attacking to the west.
Russian forces in the south appear to be focusing on a drive toward Kryvyi Rih, presumably to isolate and then take Zaporizhiya and Dnipro from the west but are unlikely to secure any of those cities in the coming weeks if at all. Kryvyi Rih is a city of more than 600,000 and heavily fortified according to the head of its military administration. Zaporizhiya and Dnipro are also large. The Russian military has been struggling to take Mariupol, smaller than any of them, since the start of the war with more combat power than it is currently pushing toward Kryvyi Rih. The Russian advance on that axis is thus likely to bog down as all other Russian advances on major cities have done.
The Russian military continues to commit small groups of reinforcements to localized fighting rather than concentrating them to launch new large-scale operations. Russia continues to commit units drawn from its naval infantry from all fleets, likely because those units are relatively more combat-ready than rank-and-file Russian regiments and brigades. The naval infantry belonging to the Black Sea Fleet is likely the largest single pool of ready reserve forces the Russian military has not yet committed. Much of that naval infantry has likely been embarked on amphibious landing ships off the Odesa coast since early in the war, presumably ready to land near Odesa as soon as Russian forces from Crimea secured a reliable ground line of communication (GLOC) from Crimea to Odesa. The likelihood that Russian forces from Crimea will establish such a GLOC in the near future is becoming remote, however, and the Russian military has apparently begun using elements of the Black Sea Fleet naval infantry to reinforce efforts to take Mariupol.
The culmination of the initial Russian campaign is creating conditions of stalemate throughout most of Ukraine. Russian forces are digging in around the periphery of Kyiv and elsewhere, attempting to consolidate political control over areas they currently occupy, resupplying and attempting to reinforce units in static positions, and generally beginning to set conditions to hold in approximately their current forward positions for an indefinite time. Maxar imagery of Russian forces digging trenches and revetments in Kyiv Oblast over the past several days supports this assessment.[1] Comments by Duma members about forcing Ukraine to surrender by exhaustion in May could reflect a revised Russian approach to ending this conflict on terms favorable to Moscow.
Stalemate will likely be very violent and bloody, especially if it protracts.
(Hat tip: Chuck Devore.)
Lots of problems, including a reiteration of the inability of the Russian air force to conduct combined arms operations, especially given their limited flight training (8 hours a month).
#Russia's active tank fleet is actually not 12,000 strong. In reality it is just over 2,500. By active tanks I mean tanks that are actually in service in an organised unit (i.e. a tank battalion, regiment, brigade etc.) and are not undergoing field tests (T-14 Armata). pic.twitter.com/fJYrGjc5L4
— TankDiary (@TankDiary) March 19, 2022
Lots of tweets wonder aloud why there have been no confirmed T-14 Armata sightings in theater in Ukraine. We’ll know Russia is really desperate if they start hauling T-64s out of mothballs and into service. (Ukraine actually has a lot of modernized T-64 Bulats, as the original T-64 factory is there.)
And since we’re talking hypersonic and eastern Europe:
St Petersburg, Russia tonight chanting "No to war", "Shame", and "Ukraine is not our enemy!" Russia has been arresting protesters all day and yet the crowd has grown. pic.twitter.com/V6ZtOIam2t
— Nick Oliva (@nick_watermn) March 16, 2022
Will the international community’s sanctions succeed in bringing Russia to heel? Completely cutting them off from the world banking system has the potential to do a lot more damage to Russian oligarchs than previously, but it’s important to remember that the Russian economy was already sucking.
Some takeaways:
Russia’s war against Ukraine grinds on. Here’s the Livemap snapshot:
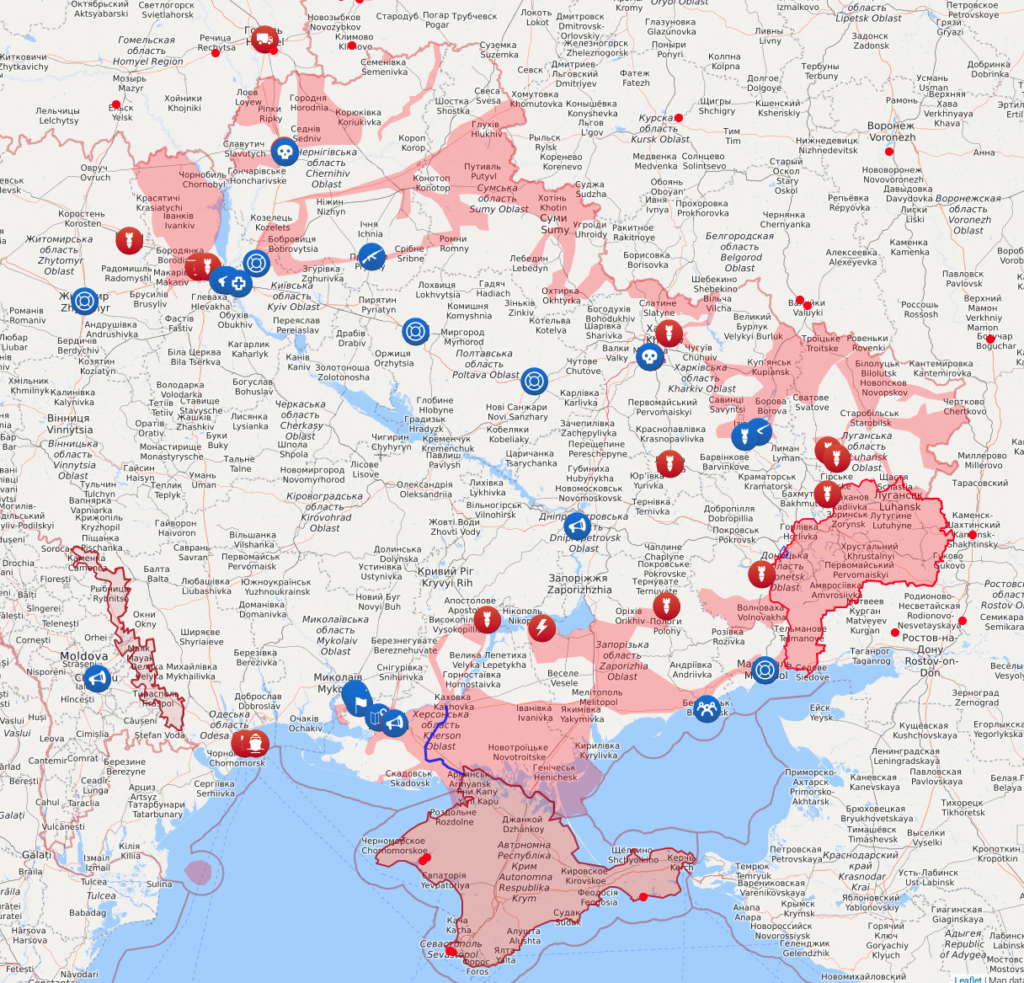
Given the usual caveats (the map is not the territory), it doesn’t seem like Russia has made much progress since my last update. Russian forces are taking high casualties as they creep closer to Kiev, and Mariupol is still in Ukrainian hands.
Some perspective on the timelines of previous mechanized invasions:
We’re now some 22 days into the Russian invasion of Ukraine, and its make other widescale mechanized land invasions look far more competent and successful.
Now the links:
- Russia is deploying reserves from Armenia and South Ossetia and cohering new battalion tactical groups (BTGs) from the remnants of units lost early in the invasion. These reinforcements will likely face equal or greater command and logistics difficulties to current frontline Russian units.
- President Zelensky created a new joint military-civilian headquarters responsible for the defense of Kyiv on March 15.
- Russian forces conducted several failed attacks northwest of Kyiv and no offensive operations northeast of Kyiv on March 16.
- Russian forces continue to shell civilian areas of Kharkiv, but will be unlikely to force the city to surrender without encircling it—which Russian forces appear unable to achieve.
- Russian forces continued to reduce the Mariupol pocket on March 16. Russian forces continue to commit war crimes in the city, targeting refugees and civilian infrastructure.
- Ukrainian Forces claimed to have killed the commander of the 8th Combined Arms Army’s 150th Motor Rifle Division near Mariupol on March 15. If confirmed, Miyaev would be the fourth Russian general officer killed in Ukraine; his death would be a major blow to the 150th Motor Rifle Division, Russia’s principal maneuver unit in Donbas.
- Russian warships shelled areas of Odesa Oblast on March 16 but Russian Naval Infantry remain unlikely to conduct an unsupported amphibious landing.
(Hat tip: The Ethereal Voice.)
In 36 days of fighting on Iwo Jima during World War II, nearly 7,000 Marines were killed. Now, 20 days after President Vladimir V. Putin of Russia invaded Ukraine, his military has already lost more soldiers, according to American intelligence estimates.
The conservative side of the estimate, at more than 7,000 Russian troop deaths, is greater than the number of American troops killed over 20 years in Iraq and Afghanistan combined.
It is a staggering number amassed in just three weeks of fighting, American officials say, with implications for the combat effectiveness of Russian units, including soldiers in tank formations. Pentagon officials say a 10 percent casualty rate, including dead and wounded, for a single unit renders it unable to carry out combat-related tasks.
With more than 150,000 Russian troops now involved in the war in Ukraine, Russian casualties, when including the estimated 14,000 to 21,000 injured, are near that level. And the Russian military has also lost at least three generals in the fight, according to Ukrainian, NATO and Russian officials.
Pentagon officials say that a high, and rising, number of war dead can destroy the will to continue fighting. The result, they say, has shown up in intelligence reports that senior officials in the Biden administration read every day: One recent report focused on low morale among Russian troops and described soldiers just parking their vehicles and walking off into the woods.
Insert the usual “anonymous sources” caveat. Though I suspect the estimates of overall Russian deaths is on the low side.
We’re witnessing a particularly unexpected set of circumstances.
One: The vaunted Russian army is proving to be a shadow of its former self.
While the Russian pounding of Ukrainian cities increases, Kyiv remains in Ukrainian control, and Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelensky is still, at minimum, safe enough to record videos of himself walking to a hospital to visit wounded Ukrainian soldiers. In just three weeks, the Russian military has likely suffered more killed, wounded, and captured than the U.S. and U.K. did combined over the course of 20 years in Afghanistan. One site attempting to track the damage calculates that the Ukrainians have destroyed, damaged, or captured more than 1,200 Russian military vehicles and shot down or otherwise damaged 15 helicopters, 13 fixed-wing aircraft, six drones, two fuel trains, and more than 400 support vehicles.
If the Russian army was marching across Ukraine as planned, the Russians would not be attempting to recruit Syrian mercenaries.
This doesn’t mean that 200,000 Russian troops, with all their support vehicles, tanks, artillery, guided-missile systems, jets, helicopters, etc., cannot kill many Ukrainians and inflict extraordinary damage on the cities and homes and critical infrastructure of Ukraine. But it does mean that the Russian army is hampered by severe logistics problems, poor intelligence and tactics, persistent communications problems, awful morale, faulty equipment, and long-expired rations. Some significant portion of the great fortune that Russia spent to upgrade its military over the past two decades was skimmed off the top and diverted into someone’s pockets.
Polina Beliakova, a senior research fellow at the Center for Strategic Studies at Tufts University, contends that Putin’s wealthy allies were stealing from the military and shortchanging the troops right under Putin’s nose:
Most companies responsible for providing food to the Russian military are connected to Yevgeny Prigozhin — the patron of PMC Wagner, the mercenary organization, and sponsor of the Internet Research Agency, which has been accused of meddling in the United States elections. Several years ago, Prigozhin’s companies were accused by Russian opposition leader Alexei Navalny of forming a cartel and gaming the state’s bidding system for defense orders, receiving contracts for several hundred million dollars. The quality of food and housing in the Russian military is reportedly worse than in its prisons, with unreasonably small meals and some carrying harmful Escherichia coli bacteria.
Putin is now learning that hard lesson of former U.S. secretary of defense Donald Rumsfeld, “You go to war with the army you have, not the army you might want or wish to have at a later time.”
The army Russia has is nowhere near as effective as Putin thought it was. And the Eastern Europeans have noticed:
“Today what I have seen is that even this huge army or military is not so huge,” said Lt. Gen. Martin Herem, Estonia’s chief of defense, during a news conference at an air base in northern Estonia with Gen. Mark A. Milley, the chairman of the U.S. Joint Chiefs of Staff. General Herem’s colleague and the air force chief, Brig. Gen. Rauno Sirk, in an interview with a local newspaper, was even more blunt in his assessment of the Russian air force. “If you look at what’s on the other side, you’ll see that there isn’t really an opponent anymore,” he said.
Two: The Russian economy continues to freefall.
The Russian government announced that they intend to pay back their debts in now-almost-worthless rubles. The Moscow Stock Exchange will stay closed until at least March 18. The Financial Times’ European banking correspondent, Owen Walker, says the Russian Ministry of Finance can keep the big Russian banks going for a while, but in the end, the Russian companies will have no money coming in from countries enacting sanctions.
Maybe India can help with this problem, but it will cost Russia; the Indian government is reportedly interested in buying Russian oil at a discount. Russia not only wants economic assistance from China, but has reportedly asked for military assistance as well, in the form of drones.
Three: Despite all of this, Putin is not only undeterred, he wants to double down.
Back in 2014, when Russian military forces moved into Crimea and annexed it, then-secretary of state John Kerry and other Obama administration officials kept talking up the option of a “diplomatic off-ramp” that would end Russia’s military occupation. Those proposals never went anywhere; Kerry seemed to be in denial of the fact that Putin was on precisely the highway he wanted to be on, headed toward exactly the destination he wanted. Putin wasn’t looking for an “off-ramp.”
Today, you hear the same refrain — that if the West just tried hard enough, it could find some “diplomatic off-ramp” that would be acceptable to Putin:
Axios: “President Biden now faces a great unanswered question — how to give Vladimir Putin an off-ramp to avoid even greater calamity.” The Irish Times: “While the prospect of a ceasefire in the short-term may seem remote, there will come a point where Putin needs an off-ramp. The West can keep applying pressure on Putin while showing him that a negotiated peace is there for the taking.” NPR: “Diplomats are trying to find an off ramp to Putin’s war in Ukraine.”
How can Putin make it any clearer? He doesn’t want an “off ramp!” He doesn’t want to end his war, he wants to win his war. He doesn’t care how gargantuan a price he or his country must pay in blood and treasure to achieve victory. To a certain degree, Putin is dealing with the sunken-cost fallacy. He has already committed so much, nationally and personally, into this war that he cannot accept a relatively modest prize of Donetsk and Luhansk and a guarantee that Ukraine would never join NATO. Russia’s big sacrifices in this war means Putin must bring home a big prize to justify the bloody endeavor.
1. Vladimir Putin may be unable to achieve his expected goals, which puts Russia in a tight spot. The purpose of Putin’s attack was to completely solve the Ukrainian problem and divert attention from Russia’s domestic crisis by defeating Ukraine with a blitzkrieg, replacing its leadership, and cultivating a pro-Russian government. However, the blitzkrieg failed, and Russia is unable to support a protracted war and its associated high costs. Launching a nuclear war would put Russia on the opposite side of the whole world and is therefore unwinnable. The situations both at home and abroad are also increasingly unfavorable. Even if the Russian army were to occupy Ukraine’s capital Kyiv and set up a puppet government at a high cost, this would not mean final victory. At this point, Putin’s best option is to end the war decently through peace talks, which requires Ukraine to make substantial concessions. However, what is not attainable on the battlefield is also difficult to obtain at the negotiating table. In any case, this military action constitutes an irreversible mistake.
2. The conflict may escalate further, and the West’s eventual involvement in the war cannot be ruled out. While the escalation of the war would be costly, there is a high probability that Putin will not give up easily given his character and power. The Russo-Ukrainian war may escalate beyond the scope and region of Ukraine, and may even include the possibility of a nuclear strike. Once this happens, the U.S. and Europe cannot stay aloof from the conflict, thus triggering a world war or even a nuclear war. The result would be a catastrophe for humanity and a showdown between the United States and Russia. This final confrontation, given that Russia’s military power is no match for NATO’s, would be even worse for Putin.
3. Even if Russia manages to seize Ukraine in a desperate gamble, it is still a political hot potato. Russia would thereafter carry a heavy burden and become overwhelmed. Under such circumstances, no matter whether Volodymyr Zelensky is alive or not, Ukraine will most likely set up a government-in-exile to confront Russia in the long term. Russia will be subject both to Western sanctions and rebellion within the territory of Ukraine. The battle lines will be drawn very long. The domestic economy will be unsustainable and will eventually be dragged down. This period will not exceed a few years.
4. The political situation in Russia may change or be disintegrated at the hands of the West. After Putin’s blitzkrieg failed, the hope of Russia’s victory is slim and Western sanctions have reached an unprecedented degree. As people’s livelihoods are severely affected and as anti-war and anti-Putin forces gather, the possibility of a political mutiny in Russia cannot be ruled out. With Russia’s economy on the verge of collapse, it would be difficult for Putin to prop up the perilous situation even without the loss of the Russo-Ukrainian war. If Putin were to be ousted from power due to civil strife, coup d’état, or another reason, Russia would be even less likely to confront the West. It would surely succumb to the West, or even be further dismembered, and Russia’s status as a great power would come to an end.
II. Analysis of the Impact of Russo-Ukrainian war On International Landscape
1. The United States would regain leadership in the Western world, and the West would become more united. At present, public opinion believes that the Ukrainian war signifies a complete collapse of U.S. hegemony, but the war would in fact bring France and Germany, both of which wanted to break away from the U.S., back into the NATO defense framework, destroying Europe’s dream to achieve independent diplomacy and self-defense. Germany would greatly increase its military budget; Switzerland, Sweden, and other countries would abandon their neutrality. With Nord Stream 2 put on hold indefinitely, Europe’s reliance on US natural gas will inevitably increase. The US and Europe would form a closer community of shared future, and American leadership in the Western world will rebound.
2. The “Iron Curtain” would fall again not only from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea, but also to the final confrontation between the Western-dominated camp and its competitors. The West will draw the line between democracies and authoritarian states, defining the divide with Russia as a struggle between democracy and dictatorship. The new Iron Curtain will no longer be drawn between the two camps of socialism and capitalism, nor will it be confined to the Cold War. It will be a life-and-death battle between those for and against Western democracy. The unity of the Western world under the Iron Curtain will have a siphon effect on other countries: the U.S. Indo-Pacific strategy will be consolidated, and other countries like Japan will stick even closer to the U.S., which will form an unprecedentedly broad democratic united front.
3. The power of the West will grow significantly, NATO will continue to expand, and U.S. influence in the non-Western world will increase. After the Russo-Ukrainian War, no matter how Russia achieves its political transformation, it will greatly weaken the anti-Western forces in the world. The scene after the 1991 Soviet and Eastern upheavals may repeat itself: theories on “the end of ideology” may reappear, the resurgence of the third wave of democratization will lose momentum, and more third world countries will embrace the West. The West will possess more “hegemony” both in terms of military power and in terms of values and institutions, its hard power and soft power will reach new heights.
Nor is he thrilled at China’s chance might fare in this scenario:
4. China will become more isolated under the established framework. For the above reasons, if China does not take proactive measures to respond, it will encounter further containment from the US and the West. Once Putin falls, the U.S. will no longer face two strategic competitors but only have to lock China in strategic containment. Europe will further cut itself off from China; Japan will become the anti-China vanguard; South Korea will further fall to the U.S.; Taiwan will join the anti-China chorus, and the rest of the world will have to choose sides under herd mentality. China will not only be militarily encircled by the U.S., NATO, the QUAD, and AUKUS, but also be challenged by Western values and systems.
His advice to China? Cut Putin loose and join the west:
China cannot be tied to Putin and needs to be cut off as soon as possible. In the sense that an escalation of conflict between Russia and the West helps divert U.S. attention from China, China should rejoice with and even support Putin, but only if Russia does not fall. Being in the same boat with Putin will impact China should he lose power. Unless Putin can secure victory with China’s backing, a prospect which looks bleak at the moment, China does not have the clout to back Russia. The law of international politics says that there are “no eternal allies nor perpetual enemies,” but “our interests are eternal and perpetual.” Under current international circumstances, China can only proceed by safeguarding its own best interests, choosing the lesser of two evils, and unloading the burden of Russia as soon as possible. At present, it is estimated that there is still a window period of one or two weeks before China loses its wiggle room. China must act decisively.
The Russians are in trouble, and they know it. That’s why they have reached out to China for help and why they are now recruiting Syrians.
Russian generals are running out of time, ammunition, and manpower. That’s not based on any inside intelligence — it’s clear from open source information and my own experience. I could be way off, but I am confident of this assessment.
An essential caveat to my assessment is that we, the West, led by the US, must accelerate and expand the support we are providing to Ukraine on the scale and with the sense of urgency of the Berlin Airlift (June 1948-May 1949). They need the weapons and ammunition to destroy the rockets, cruise missiles, and long-range artillery that are causing most of the damage to Ukrainian cities, as well as the intelligence to locate those systems, and the ability to hit Russian Navy vessels that are launching cruise missiles into cities from the Black Sea and the Azov Sea.
The time challenge for Russia is not just military. The effects of sanctions are growing — Russia may soon default on $150bn of foreign currency debt —and Russian domestic resentment is also growing (we should remember that it’s unusual as well as extreme brave for ordinary people to protest in Putin’s Russia and for television editors to suddenly interrupt their own programs waving anti-war placards.) We should do all we can to fuel that discontent and to let courageous Russians know they have our support.
Ammunition shortages
The Russians are experiencing ammunition shortages. Their transition to attrition warfare is driving up consumption rates beyond what they had planned and what they can sustain. They will still have a lot of the conventional artillery and so-called dumb bombs. But as we know from past US military operations, the most sophisticated munitions are very expensive and so more limited in availability. The Russians are likely to be having the same experience; in addition, they thought the campaign would end within a few days so large stocks were probably not prepared. Wartime consumption always exceeds planning numbers, and urban combat exacerbates that. Sanctions will also have assisted —Finland and Slovenia used to provide some munitions to Russia, and those have now stopped.
Manpower shortages
The Pentagon has said that 50% of Russian combat power was committed in Ukraine. At the height of our wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, we were about 29% committed. And it was difficult to sustain that.
This plays directly into the discussion of the encirclement of Kyiv. Russia does not have the manpower or firepower to encircle the Ukrainian capital, let alone capture it. I have been to Kyiv several times. I was there in Kyiv five weeks ago, met President Zelenskyy. It is a very large, dense major urban center on the banks of one of Europe’s largest rivers. It is a difficult, complex urban terrain.
The Ukrainians are going to be able to keep it open and prevent encirclement, especially if we can get the flow of weapons and ammunition up to the levels needed. There will be, unfortunately, be increasing attacks on the city by air and ground systems, and many more innocent Ukrainian citizens will be murdered, injured, or displaced. But I don’t believe it will fall.
Russia’s dilemma is only worsened by its combat casualties. Although I am always skeptical about enemy body counts, I do believe the numbers of dead are in the thousands (possibly in the 5,000-6,000 range suggested by US sources) and the numbers of wounded much higher. The modern battlefield is extremely lethal, especially for poorly trained or disciplined soldiers. These are very high numbers for just the first two weeks of war and many come from Russia’s elite units — they are hard to replace (and the Kremlin won’t be able to conceal these losses from the Russian public and all those for long.)
Reports of low morale, dissension between commanders, mutiny on at least one vessel, desertion, and so on, all within the first two weeks are indicators of major manpower problems. And in pure numbers, the Ukrainian armed forces still outnumber or closely match Russian forces actually on the ground in Ukraine.
There is no suggestion that the Russians have big units lurking in the woods somewhere (and the Pentagon has said it sees no signs of significant reinforcements.) So it’s apparent that the notional 900,000 strength of the Russian military is a hollow number. Their public call for 16,000 troops from Syria and elsewhere indicates this. Employment of “stop loss” by Russia on conscripts whose time is about up is another indicator. The Ukrainian diaspora is flocking home to help the fight; Russians are not coming back home — and indeed, many are leaving to avoid Putin’s fight.
Russia paused its offensive in Ukraine in recent days in order to rush in reinforcements and rebuild shattered units.
The problem, for the Kremlin, is that Ukraine is doing the same—and potentially to much greater effect. As the wider war in Ukraine enters its fourth week, the Russian army might be able to restore some of the combat power it has lost to poor planning, poorer execution and heroic resistance by the Ukrainian armed services.
But Ukraine almost certainly can double its fighting strength.
That mobilization imbalance, the consequence of strong foreign support for Kyiv, the natural logistical advantages any defender enjoys against an attacker and—most importantly—Ukrainians’ incredible determination to fight, has led one analyst to a perhaps surprising conclusion.
Russia “can’t win this war,” wrote Tom Cooper, an author and expert on the Russian military.
The Russian army built up a force of nearly 200,000 troops with thousands of armored vehicles before launching its assault on southern, eastern and northern Ukraine on the night of Feb. 23.
The invasion force encountered stiff resistance. Not only from the 145,000-person regular Ukrainian army, but also local territorial defense forces and even everyday people who improvised weaponry or found other ways to slow the Russians. Digging ditches. Destroying bridges. Texting Ukrainian artillery units with the locations of approaching Russian tanks.
As the war enters its fourth week, the Russian offensive has stalled. And the scale of Russian losses is becoming clear. The Kremlin on March 2 copped to losing fewer than 500 troops killed in action and another 1,500 wounded. The Ukrainian defense ministry a few days ago posited a much higher total: a combined 12,000 Russians “lost”—presumably meaning killed, wounded or captured.
From the perspective of someone who actually trained Ukrainian troops in Ukraine, commanded US forces, and attended the US Army War College – though it’s kind of the Chico State of war colleges – the whole way our elite is approaching the crisis is an epic clusterfark. Don’t believe anything anyone tells you – and certainly, sanity check whatever I’m telling you, too – most of these insta-experts on intra-Slavic conflict know absolutely squat-ski. Moreover, their remarkably dumb observations and credulous acceptance of conventional wisdom, which has proven long on conventional and short on wisdom, are being presented without any kind of strategic context. They don’t know where this crisis came from and certainly have no clear notion of where they want it to go beyond the vague and unhelpful idea that they want Putin (which they use interchangeably with Russia) to “lose” without knowing what that even means.
Biases are important, and here are mine. I sympathize with the Ukrainian people, partly because I worked with them and partly because I was an end-stage Cold Warrior who came up training to fight Russians. I understand that this mess is not merely the result of Putin being bad or Trump being insufficiently anti-Putin, like LTC Sausage and the rest of the failed foreign policy elite and regime media insist. Putin’s badness plays a part, but he’s merely exploiting thousands of years of bloody history, of ethnic hatred, and of Orthodox mysticism, as well as totally misguided and poorly-considered Western interference. The idea that we could just make Ukraine part of NATO and the Russians would just lump it is remarkable for its dumbness, but it is fully in keeping with our foreign policy elite’s unbroken track record of failure since the old-school military’s victory in the Gulf War…
The expectation was that the Russian forces would smash through, surround the Ukrainian forces pinned down facing the Russians in the occupied regions to the east, and isolate the main cities. I did not expect them to go into the cities immediately since Russians 1) generally bypass hard defenses; 2) they have bad experiences with city fighting (Stalingrad, Grozny); and 3) that would not necessarily be necessary. It would not be necessary if the idea was to neutralize the main Ukrainian combat formations and force the government in the cities to capitulate, then have the West pressure the Ukrainians to accept a ceasefire and “peace” that recognized Russian gains and ended the idea of Ukrainian allying with the West. In fact, that is pretty much what the Russian “peace plan” consists of. But that did not work for a couple of reasons.
First, the Russians did not fight as well as expected. You should always treat the enemy as if it is the best possible enemy. We did in the Gulf. We prepared to fight elite Republican Guard divisions of highly trained and motivated soldiers using top-shelf Soviet equipment and tactics. None of that was so; we crushed an entire national army in 100 hours.
The Russians are poorly-led, with very weak synchronization among maneuver forces and fires. Their plan is okay – in fact, you look at a map, and it’s obvious what they would do. But their gear is badly-maintained, and their troops are unsuited to the task of supporting a rapid advance. Look at all the evidently intact gear simply abandoned by the side of the road. Lots of it looks like it broke down (note all the flat tires). Much of it seems to have run out of gas. And, of course, lots of stuff had been blasted apart.
That’s the second part of the equation – the Ukrainians fought back hard. If you are a Lord of the Rings nerd, think of the Ukrainians as the dwarves. Not super-sophisticated but tough and ready to fight, and also often drunk.
If you want to see the future of this war, look at videos of Ukrainian infantry patrolling near the front. Every second guy has an anti-tank weapon, like a Javelin or some other system, and the rest are carrying spare missiles. Mechanized forces unprotected by infantry are vulnerable to ambush by anti-tank teams. The Russian armor outstripped its ground pounders and is getting pounded itself. Further, Ukrainians seem to have success with drones firing anti-tank weapons. The war is not going to be won by conventional battalions of Ukrainians operating with conventional aircraft. It will win with light infantry and drones armed with missiles.
Russian soldiers have shot people dead in the street as they took over Ukrainian villages, according to fleeing residents.
Soldiers shot randomly at buildings, threw grenades down roads and went from house to house confiscating phones and laptops, witnesses said.
Online groups created for family members or friends looking for information about people in affected areas are receiving hundreds or even thousands of requests a day.
One witness, Mykola, described how soldiers arrived in Andriivka, a village near Kyiv. “They threw grenades down the street. One man lost his leg and the next day this person died,” he said. “They then came down the central street and started shooting at the windows and hit one woman. Her children managed to hide.”
Mykola lived within walking distance of his brother, Dymtro. “My brother came out the house with his hands in the air. They beat him and then executed him in the street,” he said.
Dymtro’s wife said she saw the killing of her husband from a window. She said she also witnessed their neighbour being killed in the same manner. Dymtro’s daughter believes both were shot because they had earlier helped the Ukrainian army as volunteers.
Mykola said they wanted to bury his brother, but his wife feared the soldiers would shoot them. “The next day they went house by house, confiscating phones and laptops,” he said. At this point, 3 March, there was no electricity. “Those who came into our house behaved OK. But they told us that it’s good you have a cellar, collect some water, because you’re going to be bombed for six days.”
On Monday, United Nations secretary general António Guterres warned that, “Raising the alert level of Russian nuclear forces is a bone-chilling development. The prospect of nuclear conflict, once unthinkable, is now back within the realm of possibility.”
As hyperbolic as that claim may seem, the circumstances that would spur the Russians to use a tactical nuclear weapon are starting to fall into place. As laid out yesterday, the war is going badly for the Russians. Advances are moving slowly, when they’re moving at all, and casualties are mounting. The Russian economy is collapsing. Something’s going to break; it’s just a question of what breaks first.
This newsletter has repeatedly discussed the official Russian military doctrine, “escalate to deescalate” — that is, “If Russia were subjected to a major non-nuclear assault that exceeded its capacity for conventional defense, it would ‘de-escalate’ the conflict by launching a limited — or tactical — nuclear strike.” In other words, Russia’s official strategy when losing a war is to escalate it by using tactical battlefield nukes in order to “deescalate” it on terms favorable to Russia.
It isn’t likely that Russia will launch or detonate a tactical nuclear weapon yet. But it also isn’t unimaginable anymore. Apparently, Putin and the Russian military have been thinking about this option for a long time. In 2014, Ukrainian defense minister Valeriy Heletey said that, “The Russian side has threatened on several occasions across unofficial channels that, in the case of continued resistance they are ready to use a tactical nuclear weapon against us.”
This assumes, of course, his nukes still work. The United States is going to spend some $634 billion this decade maintaining its nuclear deterrent. Put it another way, the U.S. spends more money maintaining nuclear weapons in a given year than Russia spends annually on its entire military. Thermonuclear weapons (not fission-only tactical nuclear weapons) require regular Tritium refresh. Fission weapons still require battery and explosive refresh, and I’m not clear on the schedule.
A rapid Russian advance into the strategic southern town of 35,000 people, a gateway to a Ukrainian nuclear power station and pathway to attack Odessa from the back, would have showcased the Russian military’s abilities and severed Ukraine’s key communications lines.
Instead, the two-day battle of Voznesensk, details of which are only now emerging, turned decisively against the Russians. Judging from the destroyed and abandoned armor, Ukrainian forces, which comprised local volunteers and the professional military, eliminated most of a Russian battalion tactical group on March 2 and 3.
The Ukrainian defenders’ performance against a much-better-armed enemy in an overwhelmingly Russian-speaking region was successful in part because of widespread popular support for the Ukrainian cause—one reason the Russian invasion across the country has failed to achieve its principal goals so far. Ukraine on Wednesday said it was launching a counteroffensive on several fronts.
#Ukraine: Russian forces abandoned a PAK-200 field kitchen truck.
As you can see, it doesn't look very pleasant inside. pic.twitter.com/Az6reX2P57
— 🇺🇦 Ukraine Weapons Tracker (@UAWeapons) March 13, 2022
Other recent Russo-Ukrainian War links:
If you’ve read this previously linked article, you know that Russia is having real problems with air operations in their invasion of Ukraine. Here’s a short video that covers some of the highlights:
Key takeaways:
Thus the documented record of Ukrainian forces shooting down Russian airplanes:
#Ukraine: A Russian Su-25 jet managed to successfully land on an airfield after being hit with a Ukrainian MANPADS missile.
Guessing by the damage, the plane is likely to be decommissioned or at least will require serious repairing. pic.twitter.com/Ljv2gNkJ4m
— 🇺🇦 Ukraine Weapons Tracker (@UAWeapons) March 14, 2022
This morning Ukraine Army shot down a plane of Russian occupiers near Izyum, the pilots were ejected.#Ukraine #Russia #poland #BreakingNews #breaking #war #ukrainawar #UkraineKrieg #putin #StopPutin #stopwar pic.twitter.com/swQtMlwAwT
— Mateusz Sobieraj (@MateuszSobiera3) March 13, 2022
Helicopters too:
Russian helicopter shot down by missile in Ukrainehttps://t.co/AQ14UTxfFw pic.twitter.com/KasgRgNtmO
— BBC News (World) (@BBCWorld) March 5, 2022
(Usual propaganda cautions apply.)
Not only has Russia not achieved air superiority, these problems make it unlikely it will achieve it before the war ends.