Chris Copson of The Tank Museum has an in-depth look at the RPG-7 and its history as an effective hand-held tank-killing weapon and poor man’s artillery.
Some highlights:
Chris Copson of The Tank Museum has an in-depth look at the RPG-7 and its history as an effective hand-held tank-killing weapon and poor man’s artillery.
Some highlights:
The Russian offensive in Ukraine continues to bog down against stiff resistance, Putin puts his nukes on alert, a rumor of peace talks, momentum to suspend some Russian banks from SWIFT builds, and a whole lot of aid from the rest of the world is pouring into Ukraine.
Russia invaded Ukraine from three sides on Wednesday night Eastern time, and as of now, early afternoon Saturday, the Russian army has yet to seize any Ukrainian cities.
This morning, a senior defense official at the Pentagon briefed reporters and declared, “We continue to believe, based on what we have observed that this resistance is greater than what the Russians expected and we have indications that the Russians are increasingly frustrated by their lack of momentum over the last 24 hours particularly in the north parts of Ukraine… As of this morning we have no indication still that the Russian military has taken control over any cities. As of this morning we still believe that Russia has yet to achieve air superiority. Ukrainian air defenses including aircraft do continue to be operable and continue to engage and deny access to Russian aircraft in places over the country.”
There is an intriguing but unverified claim from Ukrainian intelligence that Putin is furious, that he expected a quick surrender from Kiev, and that the invading Russian forces weren’t equipped for a long war – and that after ten days, the Russian forces will face serious problems with supply lines, fuel, equipment, ammunition, etc. Maybe this is just Ukrainian propaganda, meant to keep up morale for the next week or so. But there are some intriguing anecdotes of Ukrainians hitting Russian supply columns and videos of Russian tanks running out of fuel. (It turns out supply chain problems are just everywhere these days!)
Sending in armored columns without dedicated infantry, artillery and air support is a big risk, big reward move. Patton did it successfully in the race across France in 1944, but he had air superiority, a friendly population, and the greatest war machine ever assembled in the history of mankind up to that time backing him, and even he had to halt when he outran his supply lines.
Putin’s initial goal, the Russian reabsorption of Ukraine or the transformation of it into a lackey state of a renewed Russian empire, is now probably impossible. Any Russian-backed Ukrainian puppet government is likely to be vehemently rejected by the Ukrainian people. Russian forces will find it difficult to go out on patrol when every citizen’s got a rifle and every grandma on every street corner is handing them sunflower seeds, telling them they are going to be fertilizer soon.
Russia may take large chunks of Ukraine, but they will have an exceptionally difficult time keeping it.
The last three days of combat should put a serious dent in the reputation of this new Russian army. We should, however, try to understand why the Russians are struggling. First, the Russian army’s recent structural reforms do not appear to have been sufficient to the task at hand. Second, at the tactical and operational level, the Russians are failing to get the most out of their manpower and materiel advantage.
There has been much talk over the last ten years about the Russian army’s modernization and professionalization. After suffering severe neglect in the ’90s, during Russia’s post-Soviet financial crisis, the army began to reorganize and modernize with the strengthening of the Russian economy under Putin. First the army got smaller, at least compared to the Soviet Red Army, which allowed a higher per-soldier funding ratio than in previous eras. The Russians spent vast sums of money to modernize and improve their equipment and kit — everything from new models of main battle tanks to, in 2013, ordering Russian troopers to finally retire the traditional portyanki foot wraps and switch to socks.
But the Russians have also gone the wrong direction in some areas. In 2008, the Russian government cut the conscription term from 24 to twelve months. As Gil Barndollar, a former U.S. Marine infantry officer, wrote in 2020:
Russia currently fields an active-duty military of just under 1 million men. Of this force, approximately 260,000 are conscripts and 410,000 are contract soldiers (kontraktniki). The shortened 12-month conscript term provides at most five months of utilization time for these servicemen. Conscripts remain about a quarter of the force even in elite commando (spetsnaz) units.
As anyone who has served in the military will tell you, twelve months is barely enough time to become proficient at simply being a rifleman. It’s nowhere near enough time for the average soldier to learn the skills required to be an effective small-unit leader.
Yes, the Russians have indeed made efforts to professionalize the officer and the NCO corps. Of course, non-commissioned officers (NCOs) have historically been a weakness of the Russian system. In the West, NCOs are the professional, experienced backbone of an army. They are expected to be experts in their military speciality (armor, mortars, infantry, logistics, etc.) and can thus be effective small-unit commanders at the squad and section level, as well as advisers to the commanders at the platoon and company level. In short, a Western army pairs a young infantry lieutenant with a grizzled staff sergeant; a U.S. Marine Corps company commander, usually a captain, will be paired with a gunnery sergeant and a first sergeant. The officer still holds the moral and legal authority and responsibility for his command — but he would be foolish to not listen to the advice and opinion of the unit’s senior NCOs.
The Russian army, in practice, does not operate like this. A high proportion of the soldiers wearing NCO stripes in the modern Russian army are little more than senior conscripts near the end of their term of service. In recent years, the Russians have established a dedicated NCO academy and cut the number of officers in the army in an effort to put more resources into improving the NCO corps, but the changes have not been enough to solve the army’s leadership deficit.
Now, let’s talk about the Russian failures at the operational and tactical level.
It should be emphasized again that the Russian army, through sheer weight of men and materiel, is still likely to win this war. But it’s becoming more and more apparent that the Russians’ operational and tactical choices have not made that task easy on themselves.
First, to many observers, it’s simply shocking that the Russians have not been able to establish complete air superiority over Ukrainian air space. After three days of hostilities, Ukrainian pilots are still taking to the skies and Ukrainian anti-air batteries are still exacting a toll on Russian aircraft. The fact that the Russians have not been able to mount a dominant Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses (SEAD) campaign and yet are insistent on attempting contested air-assault operations is, simply put, astounding. It’s also been extremely costly for the Russians.
To compound that problem, the Russians have undertaken operations on multiple avenues of advance, which, at least in the early stages of this campaign, are not able to mutually support each other. Until they get much closer to the capital, the Russian units moving north out of Crimea are not able to help the Russian armored columns advancing on Kyiv. The troops pushing towards Kyiv from Belarus aren’t able to affect the Ukrainians defending the Donbas in the east. As the Russians move deeper into Ukraine, this can and will change, but it unquestionably made the opening stages of their operations more difficult.
Third, the Russians — possibly out of hubris — do not appear to have prepared the logistical train necessary to keep some of their units in action for an extended period of time. Multiple videos have emerged of Russian columns out of gas and stuck on Ukrainian roads.
The classic saying is “Amateurs talk about tactics, but professionals study logistics” (attributed to Marines Corps commander Gen. Robert H. Barrow, but I suspect the general sentiment is much older). An army runs on its stomach, and a modern mechanized army runs on its gas tank, and something has clearly gone wrong in with Russian logistical support for this war.
America offered to evacuate Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy. Zelenskyy replied, “The fight is here; I need ammunition, not a ride.”
Zelenskyy’s reply was reminiscent of past heroes in times of war: Gen. Anthony McAuliffe who replied in “NUTS” in response to the German demand for surrender at Bastogne during the Battle of the Bulge in 1944; and the Texans striving for independence from dictator Santa Anna’s Mexico with their “Come and Take it Flag,” which was itself appropriated from Spartan King Leonidas and his response the Persian surrender demand at the Battle of Thermopylae.
This bravery, in a day when modern communications allow all Ukrainians and the world to see it, has rallied Ukrainians to defend their nation. And now that the fighting has gone on for three days, what might that mean?
Russian President Putin is said to have assembled 200,000 troops for the invasion. It is estimated that half of them have been committed so far. Further, Putin has called on 10,000 battle-hardened Chechen mercenaries. More than half of Russian forces are likely committed to the battle of Kyiv.
Ukraine has 245,000 active-duty members, but most are in the east, facing the Russian-led and equipped militia in the separatist regions of Donetsk and Luhansk. Ukraine also has another 220,000 reservists. Many of these are spread across the nation slightly larger than the state of Texas.
The strategic target is Kyiv and its independent government. To move the reservists to the fight, they must contend with Russian air superiority, slowing their march. More importantly, given this struggle for national survival, 7,000,000 men of military age and fit for military service are taking up arms. Every day, many more older men — and many Ukrainian women — are also being issued weapons, making Molotov cocktails, and joining the fight.
The ongoing Ukrainian mobilization means that the Russian military will soon be outnumbered most everywhere on the battlefield. The Ukrainians may not have the same level of modern equipment — missiles, jets, helicopter — but they have numbers and will power. And, the Russians need to eat, they need fuel, and ammunition — their resupply trucks must get through. They won’t, not in large enough numbers; everyday Ukrainians will see to that.
Zelensky: ‘We successfully fought off enemy attacks. We are defending our country, our land, future of our children. Kyiv & key places near the capital are under our control. The occupiers wanted to capture our capital and install their puppets like Donetsk. We broke their idea.’ pic.twitter.com/3PtnzXmPoy
— Christopher Miller (@ChristopherJM) February 26, 2022
Russian forces’ main axes of advance in the last 24 hours focused on Kyiv, northeastern Ukraine, and southern Ukraine. Russian airborne and special forces troops are engaged in urban warfare in northwestern Kyiv, but Russian mechanized forces are not yet in the capital. Russian forces from Crimea have changed their primary axes of advance from a presumed drive toward Odesa to focus on pushing north toward Zaporizhie and the southeastern bend of the Dnipro River and east along the Azov Sea coast toward Mariupol. These advances risk cutting off the large concentrations of Ukrainian forces still defending the former line of contact between unoccupied Ukraine and occupied Donbas. Ukrainian leaders may soon face the painful decision of ordering the withdrawal of those forces and the ceding of more of eastern Ukraine or allowing much of Ukraine’s uncommitted conventional combat power to be encircled and destroyed. There are no indications as yet of whether the Ukrainian government is considering this decision point.
Ukrainian resistance remains remarkably effective and Russian operations especially on the Kyiv axis have been poorly coordinated and executed, leading to significant Russian failures on that axis and at Kharkiv. Russian forces remain much larger and more capable than Ukraine’s conventional military, however, and Russian advances in southern Ukraine may threaten to unhinge the defense of Kyiv and northeastern Ukraine if they continue unchecked.
Key Takeaways
- Russia has failed to encircle and isolate Kyiv with the combination of mechanized and airborne attacks as it had clearly planned to do. Russian forces are now engaging in more straightforward mechanized drives into the capital along a narrow front along the west bank of the Dnipro River and toward Kyiv from a broad front to the northeast.
- Russian forces have temporarily abandoned failed efforts to seize Chernihiv and Kharkiv to the northeast and east of Kyiv and are bypassing those cities to continue their drive on Kyiv. Russian attacks against both cities appear to have been poorly designed and executed and to have encountered more determined and effective Ukrainian resistance than they expected.
- Russian movements in eastern Ukraine remain primarily focused on pinning the large concentration of Ukrainian conventional forces arrayed along the former line of contact in the east, likely to prevent them from interfering with Russian drives on Kyiv and to facilitate their encirclement and destruction.
- Russian forces coming north from Crimea halted their drive westward toward Odesa, and Ukrainian forces have retaken the critical city of Kherson. Some Russian troops remain west of the Dnipro River and are advancing on Mikolayiv, but the main axes of advance have shifted to the north and east toward Zaporizhie and Mariupol respectively.
- Russian forces have taken the critical city of Berdyansk from the west, threatening to encircle Mariupol even as Russian forces based in occupied Donbas attack Mariupol from the east, likely to pin defenders in the city as they are encircled.
- Russian successes in southern Ukraine are the most dangerous and threaten to unhinge Ukraine’s successful defenses and rearguard actions to the north and northeast.
- Russian troops are facing growing morale and logistics issues, predictable consequences of the poor planning, coordination, and execution of attacks along Ukraine’s northern border.
Here’s a Livemap snapshot of the conflict:
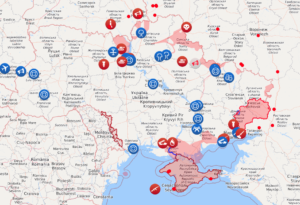
It appears that the various armored column incursions were secondary to or distractions from the attempted paratroop-powered decapitation strike to be launched from Antonov International Airport. When that went awry (as airborne assaults often do; see the SNAFU that was Operation Market Garden in World War II), there appeared to be no coherent backup plan.
Indeed, the entire operation seems to have been hastily planned and executed, which is odd, since Ukraine has obviously been much on Putin’s mind since 2014.
#Буча, ул. Вокзальная, продолжение: кто с мечом к нам пришёл, блядь, тот, блядь, от меча и погибнет #RussiaInvidedUkraine pic.twitter.com/wMMZBEtrzP
— Necro Mancer (@666_mancer) February 27, 2022
Возможно, та колонна, которую позже расколотили https://t.co/kw7o2LCmoB #Буча #RussiaInvadedUkraine
— Necro Mancer (@666_mancer) February 27, 2022
This is not the way competent troops act in hostile urban environments. It’s like the Russian army forgot all they learned from getting their asses kicked in the First Battle of Grozny, where driving ill-supported mechanized columns filled with untrained conscripts into the city resulted in horrible losses for the Russians.
The Kiev assault seems even less thought out, and their opponents appear much better equipped and trained than the Chechens were.
“As you can see, not only do Western countries take unfriendly measures against our country in the economic dimension – I mean the illegal sanctions that everyone knows about very well – but also the top officials of leading NATO countries allow themselves to make aggressive statements with regards to our country,” Putin said on state television.
“Mommy, they’re saying bad things about me!” Those unfriendly measures would, of course, stop instantly if Putin were to withdraw his forces from the territory of other sovereign nations.
Does that look or sound like an all-powerful conqueror at the top of his game? No, that’s the tone and the body language of a guy trying to explain why he just fucked up. “We had no other choice!” Yeah, except, you know, not invading another country.
Based on published NOTAMs, adding Austria, Germany, Iceland, and Italy to the list of airspace unavailable to Russian flights — all in effect by 14:00 UTC. Based statements by government officials, we expect further prohibitions on Russian flights. https://t.co/3GtCYRmZUQ pic.twitter.com/O0WTcsdRlz
— Flightradar24 (@flightradar24) February 27, 2022
Man interrupts Israeli newscast in Ukraine, becomes legend pic.twitter.com/KUlHakmdew
— Yair Rosenberg (@Yair_Rosenberg) February 27, 2022
A final word: There are a few Twitter pundits suggesting that some sort of “wag the dog” scenario of a fake war might be unfolding in Ukraine. I don’t buy it. There’s too much real reporting from too many points in Ukraine for such an elaborate, two-part deception to be unfolding. Lots of weird things happen in warfare.
I will say one thing: The manifest incompetence with which Russia has tried to carry out this assault suggests that Putin felt he had to launch it then due to some sort of time pressure or deadline, but I don’t know what it is. Maybe Putin has late stage cancer, or he felt Ukraine was about to join NATO, or a major Russian oilfield is about to run dry. Whatever it is, this war appears to be a panic move that’s gone very badly for Putin.