The answer is: “Pretty screwed.”
Some takeaways:
The answer is: “Pretty screwed.”
Some takeaways:
At this point, there seems to be no indication that Russian forces are measurably closer to their goal of controlling all of Ukraine.
Here’s a LiveMap snapshot.
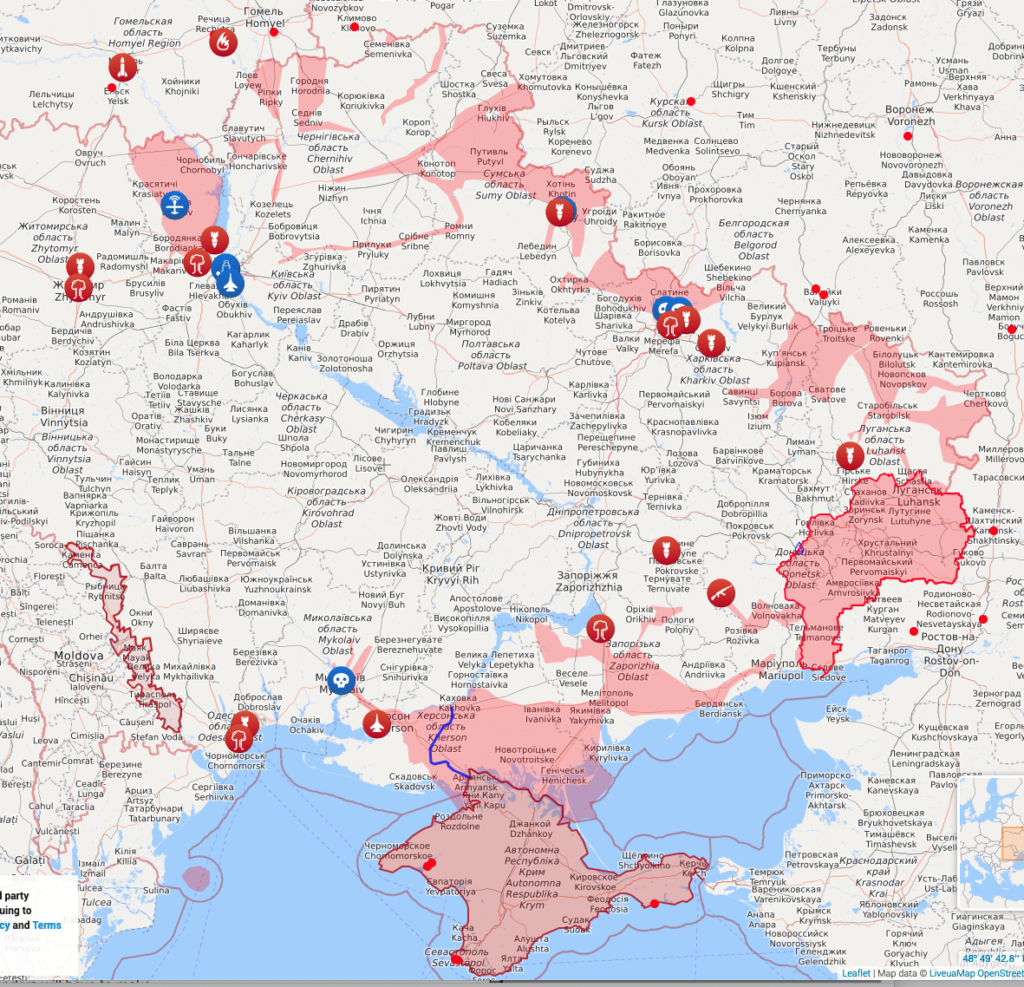
From a pure strategic viewpoint, those Russian tendrils snaking toward Kiev from the northeast look like a bad idea, since there’s no way to protect their supply lines.
(Always remember that the map is not the territory, and that both sides are working hard to put out propaganda, though the Russians seem to be manifestly incompetent at it.)
Kadyrov's squad was absolutely demolished before they even had a chance to fight and they got blown to pieces. I do not have any info that it was an FSB leak to Ukraine, so I’d give it a 1-2% chance – but can’t exclude this possibility completely.
— Igor Sushko (@igorsushko) March 6, 2022
I assume that’s Ramzan Kadyrov, corrupt head of the Chechen Republic, former resistance fighter against Russia who defected in 1999 and was appointed by Putin in 2007. Bit of a jihadist scumbag to boot, and just a generally nasty piece of work. I assume by “Kadyrov’s squad” they mean the Kadyrovtsy, the militia forces under his direct control.
Our Blitzkrieg has totally collapsed. It is impossible to complete the task: If Zelensky and his deputies were captured in the first 3 days, all key buildings also captured, and they were forced to read an address of their surrender to the country,
— Igor Sushko (@igorsushko) March 6, 2022
Some tweets about who could they even get post-Zelensky to sign a treaty (Medvechuk? Tsaryova? Yanukovich?) snipped.
2) Our logistics are already over-extended today. We can send a much large contingent into Ukraine, and what would we get? Ukraine – a territorially enormous country, and their hate towards us is astronomical.
— Igor Sushko (@igorsushko) March 6, 2022
With regards to Russian military losses: I don’t know the reality – no one does. There was some information the first 2 days, but now no one knows what is happening in Ukraine. We’ve lost contact with major divisions. (!!)
— Igor Sushko (@igorsushko) March 6, 2022
Because all of this was planned at the top (in Russia), because we were told that such a scenario will not happen (Ukraine invasion) except only if we were to be attacked first.
— Igor Sushko (@igorsushko) March 6, 2022
Now, civilian losses in Ukraine will follow a geometric pattern progression, and resistance against us will only get stronger. Infantries already tried to enter cities – out of 20 paratrooper groups, only one had “provisional” success.
— Igor Sushko (@igorsushko) March 6, 2022
Our conditional deadline is June. Conditional because in June there will be no economy left in Russia – there will be nothing left.
— Igor Sushko (@igorsushko) March 6, 2022
And so, with the Ukrainian question we lunged as if going for a 100m sprint, but turned out we’d signed up for a marathon. And this is a rather brief overview of the current events.
— Igor Sushko (@igorsushko) March 6, 2022
I don’t agree with every conclusion (I doubt the war will produce worldwide famine), but it’s still worth reading the whole thread.
Cheap Chinese tires have been blamed for a Russian convoy of armoured vehicles being unable to reach Kyiv.
Yesterday, the Ministry of Defence issued an update revealing that a convoy of Russian tanks advancing on the capital of Ukraine remained 30km from the centre of the city having made little progress over the previous three days because of “Ukranian resistance, mechanical breakdown and congestion.”
Karl Muth, an academic based at the University of Chicago and a self-described tire expert, took to Twitter to set out a theory blaming cheap Chinese tires for the slow advance of Russian vehicles.
“Those aren’t Soviet-era heavy truck radials,” Muth said, commenting on a photo of a Russian army vehicle with ripped tires.
Instead Muth believes the trucks use “Chinese military tires, and I believe specifically the Yellow Sea YS20.”
“This is a tire I first encountered in Somalia and Sudan. it’s a bad Chinese copy of the excellent Michelin XZL military tire design,” he continued.
Former pentagon staff member Trent Telenko also got stuck into the debate and said “poor Russian army truck maintenance practices” has created a risk of equipment failure.
“When you leave military truck tires in one place for months on end. The side walls get rotted/brittle such that using low tire pressure setting for any appreciable distance will cause the tires to fail catastrophically via rips,” Telenko said.
There are reportedly more than 400,000 “volunteer hackers” helping Ukraine fight its cyberwar against Russia.
Victor Zhora, deputy chief of Ukraine’s information protection service, told Bloomberg last week that Ukraine was putting up a “cyber resistance” against its invasion that would work to try and weaken Russia.
Zhora said: “Our friends, Ukrainians all over globe, [are] united to defend our country in cyberspace. [Ukraine is working to do] everything possible to protect our land in cyberspace, our networks, and to make the aggressor feel uncomfortable with their actions.”
He also said that volunteers were helping Ukraine obtain intelligence in order to fight back at Russian military systems.
They are also trying to get the message out to Russian citizens, who have been Fed a starkly different narrative from their government than the rest of the world has seen play out. Volunteers are working to “address Russian people directly by phone calls, by emails, by messages” and “by putting texts on their services and showing real pictures of war.”
There aren’t 400,000 real hackers around the world. But 10,000 hackers and 390,000 script kiddies can sill do a lot of damage…
The Russian invasion of Ukraine will end when one or more of four things breaks:
- the Russian supply lines;
- the Ukrainian ability to effectively resist;
- the Russian economy;
- the patience of some armed individuals around Putin.
We’re already seeing a lot of the first and third…
More than a week into the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Russian Air Force has yet to commence large-scale operations. Inactivity in the first few days could be ascribed to various factors, but the continued absence of major air operations now raises serious capability questions.
One of the greatest surprises from the initial phase of the Russian invasion of Ukraine has been the inability of the Russian Aerospace Forces (VKS) fighter and fighter-bomber fleets to establish air superiority, or to deploy significant combat power in support of the under-performing Russian ground forces. On the first day of the invasion, an anticipated series of large-scale Russian air operations in the aftermath of initial cruise- and ballistic-missile strikes did not materialise. An initial analysis of the possible reasons for this identified potential Russian difficulties with deconfliction between ground-based surface-to-air missile (SAM) batteries, a lack of precision-guided munitions and limited numbers of pilots with the requisite expertise to conduct precise strikes in support of initial ground operations due to low average VKS flying hours. These factors all remain relevant, but are no longer sufficient in themselves to explain the anaemic VKS activity as the ground invasion continues into its second week. Russian fast jets have conducted only limited sorties in Ukrainian airspace, in singles or pairs, always at low altitudes and mostly at night to minimise losses from Ukrainian man-portable air defence systems (MANPADS) and ground fire.
Snip.
While the early VKS failure to establish air superiority could be explained by lack of early warning, coordination capacity and sufficient planning time, the continued pattern of activity suggests a more significant conclusion: that the VKS lacks the institutional capacity to plan, brief and fly complex air operations at scale. There is significant circumstantial evidence to support this, admittedly tentative, explanation.
First, while the VKS has gained significant combat experience in complex air environments over Syria since 2015, it has only operated aircraft in small formations during those operations. Single aircraft, pairs or occasionally four-ships have been the norm. When different types of aircraft have been seen operating together, they have generally only comprised two pairs at most. Aside from prestige events such as Victory Day parade flypasts, the VKS also conducts the vast majority of its training flights in singles or pairs. This means that its operational commanders have very little practical experience of how to plan, brief and coordinate complex air operations involving tens or hundreds of assets in a high-threat air environment. This is a factor that many Western airpower specialists and practitioners often overlook due to the ubiquity of complex air operations – run through combined air operations centres – to Western military operations over Iraq, the Balkans, Libya, Afghanistan and Syria over the past 20 years.
Second, most VKS pilots get around 100 hours’ (and in many cases less) flying time per year – around half of that flown by most NATO air forces. They also lack comparable modern simulator facilities to train and practise advanced tactics in complex environments. The live flying hours which Russian fighter pilots do get are also significantly less valuable in preparing pilots for complex air operations than those flown by NATO forces. In Western air forces such as the RAF and US Air Force, pilots are rigorously trained to fly complex sorties in appalling weather, at low level and against live and simulated ground and aerial threats. To pass advanced fast jet training they must be able to reliably do this and still hit targets within five to ten seconds of the planned time-on-target. This is a vital skill for frontline missions to allow multiple elements of a complex strike package to sequence their manoeuvres and attacks safely and effectively, even when under fire and in poor visibility. It also takes a long time to train for and regular live flying and simulator time to stay current at. By contrast, most VKS frontline training sorties involve comparatively sterile environments, and simple tasks such as navigation flights, unguided weapon deliveries at open ranges, and target simulation flying in cooperation with the ground-based air-defence system. Russia lacks access to a training and exercise architecture to rival that available to NATO air forces, which routinely train together at well-instrumented ranges in the Mediterranean, North Sea, Canada and the US. Russia also has no equivalent to the large-scale complex air exercises with realistic threat simulation which NATO members hold annually – the most famous of which is Red Flag. As such, it would be unsurprising if most Russian pilots lack the proficiency to operate effectively as part of large, mixed formations executing complex and dynamic missions under fire.
Third, if the VKS were capable of conducting complex air operations, it should have been comparatively simple for them to have achieved air superiority over Ukraine. The small number of remaining Ukrainian fighters, conducting heroic air-defence efforts over their own cities, are forced to operate at low altitudes due to long-range Russian SAM systems and consequently have comparatively limited situational awareness and endurance. They ought to be relatively easily to overwhelm for the far more numerous, better armed and more advanced VKS fighters arranged around the Ukrainian borders. Ukrainian mobile medium- and short-range SAM systems such as SA-11 and SA-15 have had successes against Russian helicopters and fast jets. However, large Russian strike aircraft packages flying at medium or high altitude with escorting fighters would be able to rapidly find and strike any Ukrainian SAMs which unmasked their position by firing at them. They would lose aircraft in the process, but would be able to attrit the remaining SAMs and rapidly establish air superiority.
Russia has every incentive to establish air superiority, and on paper should be more than capable of doing so if it commits to combat operations in large, mixed formations to suppress and hunt down Ukrainian fighters and SAM systems. Instead, the VKS continues to only operate in very small numbers and at low level to minimise the threat from the Ukrainian SAMs. Down low, their situational awareness and combat effectiveness is limited, and they are well within range of the MANPADS such as Igla and Stinger which Ukrainian forces already possess. The numbers of MANPADS are also increasing, as numerous Western countries send supplies to beleaguered Ukrainian forces. To avoid additional losses to MANPADS, sorties continue to be primarily flown at night, which further limits the effectiveness of their mostly unguided air-to-ground weapons.
(Hat tip: Chuck Moss.)
But once they realised that there will be resistance and the war looks like this, their enthusiasm started declining. Which means it will be much harder to find new volunteers to go fight to Ukraine. But you need them. What are you gonna do? pic.twitter.com/ItmwcYSwIe
— Kamil Galeev (@kamilkazani) March 6, 2022
“Sources have been telling me, sources that are well connected to the Russian Security Services, that the offensive is not going well, that some special forces, the Russian Spetsnaz, are furious because they have been sent into battle without proper support, and many of them have been killed. They say that the national guard forces and the regular army, the national guard forces include those Chechen units, that two of them are not coordinating on the field. And that the overall battle plan is somewhat disjointed in that it’s partly a plan for war and partly a plan for peacekeeping and so-called de-Nazification of this country. And it has led to a lack of cohesion,” Engel reported.
“A lot of this goes back to the man who’s behind it all, Vladimir Putin, who I’m told is now increasingly isolated, is just taking advice from his inner circle, that there are only about three people who matter right now,” Engel continued. “And that speech, you mentioned it a short while ago, that Putin gave yesterday — bizarre location, speaking at Aeroflot, to a group of flight attendants. He sounded incredibly angry. He sounded detached. He was talking about how the Ukrainians here are machine-gunning people, that they’re driving around in cars packed with explosives, jihadi-style. And he went very deep and repeatedly on this theme that they’re fighting against the Nazis. It was the angriest I’ve ever seen him.”
This is from a couple of days ago. Have Spetsnaz pissed off at you doesn’t seem like a good long-term survival strategy for a Russian leader. On the other hand, this report probably deserves some skepticism, since it fits too easily into what we would like to hear about the situation, so some salt is in order. (Hat tip: Director Blue.)